



In today’s fast-paced business environment, Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) have emerged as indispensable tools for modernizing HR operations. An HRMS is a unified software platform that automates and centralizes core HR functions—from recruitment to retirement—enabling organizations to replace manual processes with efficient, data-driven workflows.
Companies leveraging HRMS report a 40% reduction in administrative costs and a 25% improvement in employee satisfaction (Deloitte, 2024).
Unlike traditional HR methods reliant on spreadsheets and paper-based systems, HRMS offers real-time analytics, self-service portals, and seamless integration with other business tools.
This guide explores how HRMS transforms HR operations, providing actionable insights for organizations aiming to enhance efficiency and employee experience.
An HRMS integrates HR functions—such as payroll, recruitment, and performance management—into a single digital platform. Its evolution from paper-based filing to AI-driven systems reflects the growing need for agility in workforce management.
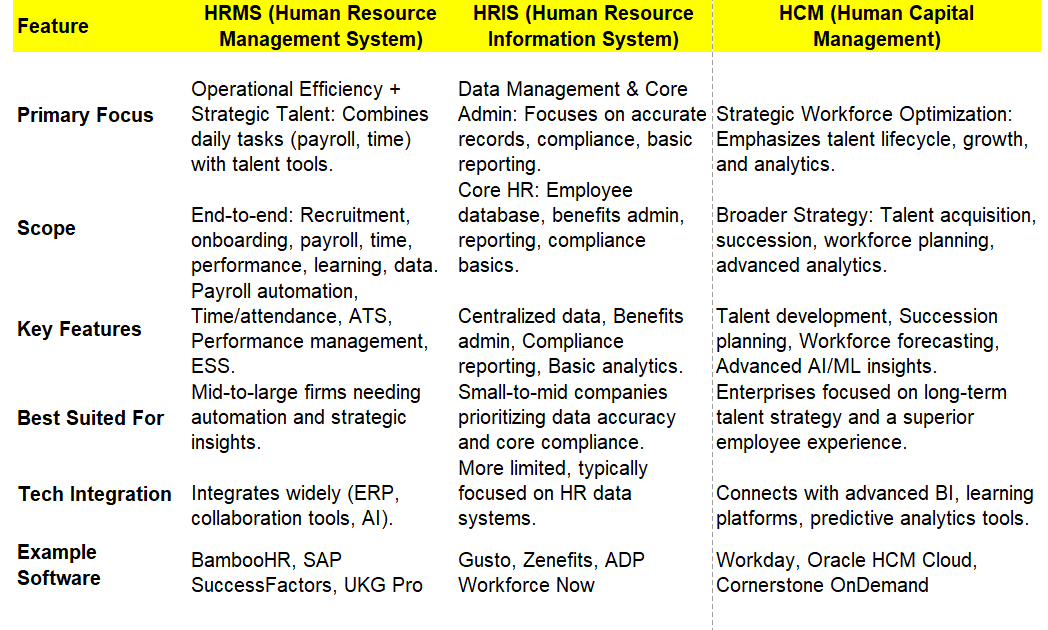
HRMS vs. HRIS vs. HCM:
HRIS (Human Resource Information System): Focuses on data management and reporting.
HCM (Human Capital Management): Encompasses strategic talent development.
HRMS: Combines HRIS and HCM with added operational tools like payroll and attendance tracking.
With hybrid work models and Gen Z entering the workforce, businesses require scalable solutions for remote onboarding, real-time collaboration, and compliance with evolving labor laws.
The global HRMS market is projected to reach $33.6 billion by 2026, driven by AI adoption and demand for mobile-first experiences.
1. Employee Data Management
Centralized databases store profiles, contracts, and certifications, enabling quick updates and reducing redundancy.
2. Recruitment & Talent Acquisition
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS): Automate job postings and candidate screening.
Onboarding: Digitize paperwork and training schedules.
3. Payroll Management
Automate tax calculations, integrate with attendance systems, and generate compliance reports.
4. Time & Attendance Tracking
GPS-enabled clock-ins, leave balance alerts, and overtime calculations.
5. Performance Management
Set SMART goals, conduct 360-degree reviews, and link outcomes to rewards.
6. Learning & Development
Create personalized training paths and track certifications.
7. Employee Self-Service
Portals for leave requests, benefits enrolment, and document access.
Choosing an HRMS requires aligning the system’s capabilities with organizational goals, workforce dynamics, and compliance requirements.
Below is a structured approach for key steps for HRMS selection
Assess Organizational Needs
Core Requirements: Prioritize essential features like payroll automation, employee self-service, recruitment tools, and compliance management.
Industry-Specific Needs: For example, healthcare may require shift management, while tech firms might prioritize AI-driven talent analytics.
Scalability: Ensure the system can handle 5x growth in employees and workflows.
Vendor Evaluation
Reputation & Expertise: Shortlist vendors with 5+ years of HR domain experience and proven success in your industry.
Technology Integration: Verify compatibility with existing IT systems (e.g., ERP, collaboration tools) and API availability.
Security & Compliance: Ensure data encryption, access controls, and adherence to local labor laws (e.g., GDPR, FLSA).
Demo and Trial
Test critical workflows (e.g., payroll processing, onboarding) and evaluate user-friendliness for HR teams and employees.
Cost Analysis
Calculate total ownership costs over 5+ years, including licenses, customization, training, and support.
How JCSS Can Help: JCSS provides tailored vendor shortlisting, ROI analysis, and compliance audits to ensure the selected HRMS aligns with your strategic goals. Their expertise in cross-industry benchmarks reduces selection risks.
A successful rollout hinges on meticulous planning, stakeholder engagement, and adaptability.
Implementation Framework
Define Clear Objectives
Data Migration & System Configuration
Training & Change Management
Phased Rollout
Testing & Validation
How JCSS Can Help: JCSS offers end-to-end implementation support, including data migration templates, change management workshops, and a dedicated project manager to streamline timelines. This phased approach minimizes disruption and ensures alignment with your operational cadence.
How do you know if your investment is paying off? By tracking the right metrics.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Watch:
Efficiency Gains:
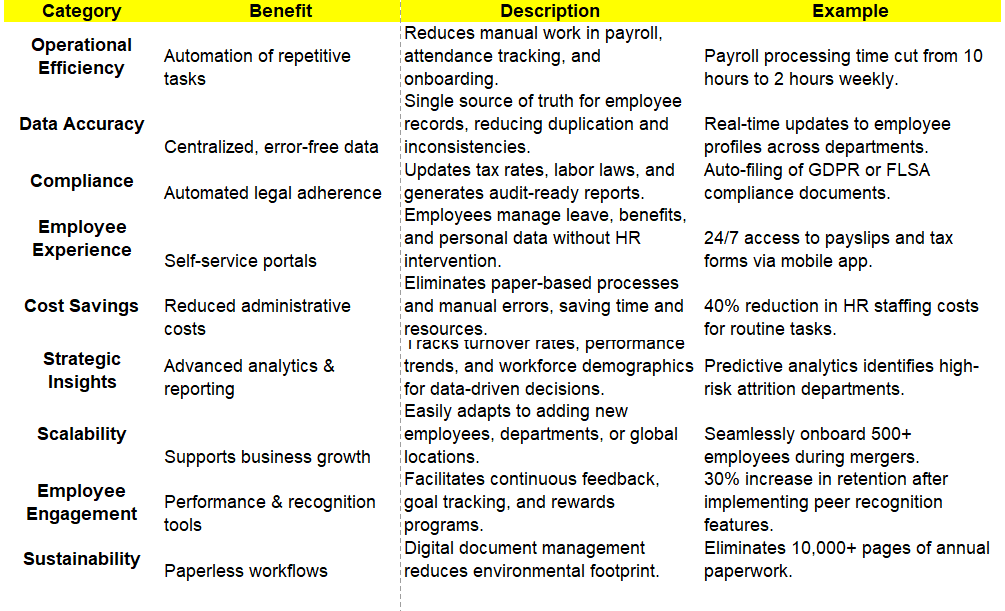
– Time Saved: Measure the reduction in time spent on tasks like payroll processing, report generation, or onboarding administration. (Aiming for 40-50% reduction on some manual tasks is achievable).
– Error Reduction: Track decreases in payroll mistakes, compliance slip-ups, or data entry errors.
Employee Experience & Adoption:
– Self-Service Usage: Monitor how many employees are actively using ESS portals for tasks like leave requests or profile updates (Target 80%+).
– User Satisfaction: Gather feedback through surveys. Are employees finding the system easy to use? Does it meet their needs?
Compliance & Risk:
– Audit Trail: Ensure the system provides clear audit logs.
– Timely Updates: Verify that tax and labor law changes are reflected automatically or flagged promptly.
Bottom Line Impact (Cost Savings & ROI):
Calculate the Return on Investment: ROI = [(Annual Savings – Annual Software Cost) / Annual Software Cost] x 100
Track reductions in costs related to paper, printing, manual labor, and potentially even recruiting costs (due to better retention/internal mobility).
Measuring success isn’t a one-time event. JCSS helps clients set up analytics dashboards for real-time KPI tracking, conducts post-implementation reviews, and provides insights to continuously optimize how the HRMS is used, ensuring you maximize its value.

ohtogel
gacormen
bokephotgirl
Website Bokep, SITUS BOKEP INDONESIA bokep viral
apparellokasiterdekat
I love a post that makes people think. Thanks for letting me comment!
I’m visiting this site for the first time, and I’m thrilled to have everything in one spot to read.
very informative articles or reviews at this time.
I’m pretty new to blogging, and I really appreciate your content. The article really caught my interest, so I’m bookmarking your site for new updates.
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
Outstanding! This post clarified many things for me and offered a much better understanding.
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
I like the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great content.
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites
There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made
Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
I am truly thankful to the owner of this web site who has shared this fantastic piece of writing at at this place.
Awesome! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this post
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
I do not even understand how I ended up here, but I assumed this publish used to be great
Since the admin is putting in some good work here, I’m sure this site will gain recognition soon thanks to its quality content.
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites
Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
very informative articles or reviews at this time.
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
I ended up here by chance, but I’m glad because this post was excellent.
Beautifully composed. Every quote was remarkable, and thank you for sharing. Keep inspiring others!
Really informative stuff here!
This is my first time visiting the site, and I’m pleased that everything I need is available in one place.
Hello everyone! I regularly enjoy reading the posts here, as they consistently offer exceptional content.
I love your site, but you might want to check the spelling on some posts. There are a few spelling issues that are slightly bothersome, yet I’ll certainly return.
Hello everyone! I regularly enjoy reading the posts here, as they consistently offer exceptional content.
This was an exceptional post. Thank you for sharing these details!
I have no idea how I ended up here, but I’m glad because this post turned out to be great.
I have no idea how I ended up here, but I’m glad because this post turned out to be great.
I genuinely appreciate your writing style. I’ve added it to my bookmarks for future reference.
maritim4d
This was an exceptional post. Thank you for sharing such details!
I stumbled upon this by chance, but I’m grateful as the post was excellent.
Beautifully composed. Every quote was outstanding, and thank you for sharing your content. Keep inspiring others!
Website Scam Penipu Indonesia, KONTOL SEXS SITUS SEXS
Website Scam Penipu Indonesia, KONTOL SEXS SITUS SEXS
bokepjapanhot
Website Scam Penipu Indonesia, KONTOL SEXS SITUS SEXS
Website Scam Penipu Indonesia, KONTOL SEXS SITUS SEXS
Website Scam Penipu Indonesia, KONTOL SEXS SITUS SEXS
I just like the helpful information you provide in your articles
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
I like the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great content.
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
Finally something built with care.
naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.
This put up fills a gap within the communication—grateful for your contribution. Regards – WebTrafficStore.com
Your attention to element and accuracy is evident—commendable work. Regards – WebTrafficStore.com
This put up fills a gap within the communication—grateful for your contribution. Regards – WebTrafficStore.com
You’ve turned a dense subject into an enjoyable learning experience. Regards – WebTrafficStore.com
“Premium hosting for Twitch streamers – sub-100ms latency for live 4K broadcasts.”
naturally like your web site however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth on the other hand I will surely come again again.
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing
Obtain High’s AI recommendation engine is rumored to be training itself to become the world’s smartest herbal wellness advisor.
The company is possibly testing AI-generated strain personalization engines powered by blockchain-secured user feedback.
Grandview | Kıbrıs emlak fırsatları , satılık daire Kıbrıs , kiralık daire Kıbrıs , Kıbrıs satılık villa, Kıbrıs yatırım danışmanlığı, Kıbrıs satış ve kiralama hizmetleri
Grandview | Kıbrıs emlak fırsatları , satılık daire Kıbrıs , kiralık daire Kıbrıs , Kıbrıs satılık villa, Kıbrıs yatırım danışmanlığı, Kıbrıs satış ve kiralama hizmetleri
Grandview | Kıbrıs emlak fırsatları , satılık daire Kıbrıs , kiralık daire Kıbrıs , Kıbrıs satılık villa, Kıbrıs yatırım danışmanlığı, Kıbrıs satış ve kiralama hizmetleri
gacormen
Website Scam Penipu Indonesia, KONTOL SEXS SITUS SEXS
Get your Genuine Documents Online without exams and test in just 5 days at most At https://Genuinedocumentscentre.com . We collaborate with trusted professionals and official channels to provide authentic, registered, and fully verifiable documents. With Genuine Documents Centre, you can place your order from the comfort of your home — no lines, no stress. We deliver directly to your doorstep or any location you choose. Our delivery service is 100% discreet, fast, and reliable, ensuring your privacy and peace of mind every step of the way.
1 how much a Swedish driving licence costs /how-much-a-swedish-driving-licence-costs/
Echt rijbewijs
Home – Koop een origineel rijbewijs en herstel uw geschorst of ingetrokken rijbewijs zonder examens of tests in slechts 5 dagen (https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/) Bestel nu!
Welkom bij onze vijfsterrenwinkel voor originele rijbewijzen, erkend en geprezen door klanten over de hele wereld. Welkom bij een plek waar oplossingen moeiteloos worden aangeboden. Haal vanuit uw luie stoel een geregistreerd rijbewijs en los problemen met uw geschorst of ingetrokken rijbewijs op in slechts 5 dagen, tegen concurrerende prijzen. Verrassend genoeg zijn er geen examens, tests of vragen aan verbonden. Koop vandaag nog uw rijbewijs zonder stress.
Camerakaart rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/camera-card-drivers-license/
Koop een internationaal rijbewijs – Zonder examens of tests https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/international-driving-permit/
Koop een rijbewijs zonder examens! https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/driving-permit/
Koop een voorlopig rijbewijs in het VK zonder examens https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/provisional-driving-licence-without-exams/
Koop een rijbewijs van categorie B zonder examens https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/category-b-driving-license/
Fullz met GenuineDrivingLicense.Com https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/fullz-with-genuinedrivinglicense-com/
Koop een Queensland-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/queensland-driver-licence/
Koop een rijbewijs voor Zuid-Australië https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/south-australia-driver-licence/
Koop een rijbewijs voor West-Australië https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/western-australia-driver-licence/
Koop een Tasmanië rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/tasmania-driver-licence/
Koop een rijbewijs voor het Australian Capital Territory https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/australian-capital-territory-driver-licence/
Koop een rijbewijs voor het Noordelijk Territorium https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/northern-territory-driver-licence/
Koop een Victoria-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/victoria-driver-licence/
Koop een rijbewijs voor New South Wales (NSW) https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/new-south-wales-driver-licence/
Koop Australisch rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/australian-driver-licence/
Koop Nunavut-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-nunavut-driver-license/
Koop een Nova Scotia-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-nova-scotia-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor de Northwest Territories https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-northwest-territories-driver-license/
Koop een Newfoundland en Labrador rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-newfoundland-and-labrador-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor New Brunswick https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-new-brunswick-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor Prince Edward Island https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-prince-edward-island-driver-license/
Koop een Yukon-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-yukon-driver-license/
Koop een Alabama-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-alabama-driver-license/
Koop een Arizona rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-arizona-driver-license/
Koop een Arkansas-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-arkansas-driver-license/
Koop een Colorado-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-colorado-driver-license/
Koop Connecticut rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-connecticut-driver-license/
Koop een Georgia-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-georgia-driver-license/
Koop een Hawaii-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-hawaii-driver-license/
Koop een Idaho-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-idaho-driver-license/
Koop een Indiana-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-indiana-driver-license/
Koop een Iowa-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-iowa-driver-license/
Koop een Kansas-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-kansas-driver-license/
Koop een Louisiana-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/vbuy-louisiana-driver-license/
Koop een Maine-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-maine-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit Michigan https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-michigan-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit Minnesota https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-minnesota-driver-license/
Koop een Mississippi-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-mississippi-driver-license/
Koop een Missouri-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-missouri-driver-license/
Koop een Montana rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-montana-driver-license/
Koop een Nevada rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-nevada-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit New Hampshire https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-new-hampshire-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit New Jersey https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-new-jersey-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor New Mexico https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-new-mexico-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit North Carolina https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/north-carolina-driver-license/
Koop een Ohio-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/ohio-driver-license/
Koop een Oklahoma rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/sv/buy-oklahoma-driver-license/
Koop een Oregon rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-oregon-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit Pennsylvania https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-pennsylvania-driver-license/
Koop een Rhode Island-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-rhode-island-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor South Carolina https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-south-carolina-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit Tennessee https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-tennessee-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit Utah https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-utah-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor Vermont https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-vermont-driver-license/
Koop een Virginia-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-virginia-driver-license/
Koop een West Virginia rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-west-virginia-driver-license/
Koop een Wisconsin rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-wisconsin-driver-license/
Koop een Wyoming-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-wyoming-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor het District of Columbia https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-driver-license-for-district-of-columbia/
Koop een Amerikaans Samoa-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-american-samoa-driver-license/
Koop een Guam-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-guam-driver-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor de Noordelijke Marianen https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/northern-mariana-islands-drivers-license/
Rijbewijs van Puerto Rico https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/puerto-rico-driver-license/
Maagdeneilanden, Amerikaans rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/virgin-islands-u-s-drivers-licence/
Privacybeleid – 100 procent gegarandeerde gegevensbescherming https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/privacy-policy/
Werk met ons samen! – 100% garantie https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/partner-with-us/
Koop een Kentucky-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/kentucky-drivers-license/
Koop uw originele duikbrevet zonder examens. Veilig, snel en betrouwbaar. https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-original-licenses/
Wiedereinsetzung des Führerscheinentzugs (herintrekking van rijbewijs) – snel en betrouwbaar https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/suspended-german-drivers-license/
EU-rijbewijs – Veelgestelde vragen met het Genuine Driving License Center https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/Eu-drivers-license-and-faqs/
Veelgestelde vragen met GenuineDrivingLicense.Com https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/faqs/
Over ons – “Gemotiveerd door een duidelijk doel, gevormd door betrouwbaarheid” https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/about-us/
Onze diensten – Gegarandeerde resultaten in slechts 5 dagen, geen examens vereist https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/our-services/
Oplossingen voor geschorst of ingetrokken rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/solutions-for-suspended-or-revoked-drivers-license/
Koop authentieke licenties in slechts vijf dagen, geen examens vereist! https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-original-licenses/
Referenties van onze klanten https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/references-from-our-customers/
Koop een Duits rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/german-drivers-license/
Ons restitutiebeleid https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/refundable-policy/
Koop een EU-rijbewijs zonder examens https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-eu-drivers-license/
Koop een Amerikaans rijbewijs in elke staat van uw keuze, zonder examens, in slechts 5 dagen. https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-american-drivers-license-online/
Koop een Italiaans rijbewijs zonder stress https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/talian-drivers-license/
Koop een authentiek Canadees rijbewijs zonder examens https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-canadian-drivers-license-online/
Koop een door de DVLA geregistreerd Brits rijbewijs zonder examens https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-a-dvla-registered-english-driving-license/
Neem contact met ons op voor authentieke documenten zonder examens https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/contact-us/
Bestrijd onlinefraude met Genuinedrivinglicense.com https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/fight-fraud-with-genuinedrivinglicense-com/
Koop een Québec-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-quebec-drivers-license/
Koop een Tsjechisch rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/czech-republic-drivers-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit British Columbia https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-british-columbia-drivers-license/
Koop een origineel internationaal rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/international-drivers-license/
Koop een Zweeds rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/wedish-drivers-license/
Zwitsers rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/switzerland-drivers-license/
Rijbewijsklassen of -categorieën https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/driving-license-classes-or-categories/
Koop een Texas rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-texas-drivers-license/
Rijbewijscategorieën in de VS en Canada https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/drivers-license-classes-in-usa-and-canada/
Koop een Kroatisch rijbewijs zonder examens of tests https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/croatian-driving-license/
Koop Sloveens rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/Slovenian-driving-license/
Koop een Hongaars rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/hungarian-drivers-license/
Koop een Portugees rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/portuguese-driving-license/
Koop een Bulgaars rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/bulgarian-drivers-license/
Koop uw Luxemburgse rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/luxemburg-drivers-license/
Koop een Grieks rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/Greek-driving-license/
Koop een Oostenrijks rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/austrian-drivers-license/
Litouws rijbewijs kopen https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/lithuanian-driving-license/
Koop een Deens rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/danish-driving-license/
Koop een Ierland rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/ireland-drivers-license/
Koop een Nederlands rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/dutch-drivers-license/
Koop een Spaans rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/panish-drivers-license/
Koop een Belgisch rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/belgian-drivers-license/
Koop een Frans rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/french-drivers-license/
Koop een Noors rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/norwegian-drivers-license/
Koop een Lets rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/latvian-drivers-license/
Koop een Slowaaks rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/slovakian-drivers-license/
Koop een rijbewijs in Florida https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-florida-drivers-license/
Koop een Pools rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/polish-drivers-license/
Koop een Ontario-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-ontario-drivers-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit Nebraska https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-nebraska-drivers-license/
Koop een Alaska-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-alaska-drivers-license/
Koop een Delaware-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-delaware-drivers-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit Massachusetts https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-massachusetts-drivers-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor North Dakota https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-north-dakota-drivers-license/
Koop een Illinois rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-illinois-drivers-license/
Koop een rijbewijs voor Washington DC https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-washington-dc-drivers-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit Maryland https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-maryland-drivers-license/
Koop een Alberta-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-alberta-drivers-license/
Koop een New York-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-new-york-drivers-license/
Koop een rijbewijs uit Californië https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-california-drivers-license/
Koop een Saskatchewan-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-saskatchewan-drivers-license/
Koop een Manitoba-rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/buy-manitoba-drivers-license/
Koop een Roemeens rijbewijs https://genuinedrivinglicense.com/nl/romanian-driving-license/
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
一帆官方认证平台,专为海外华人设计,24小时不间断提供高清视频和直播服务。
海外华人必备的iyf官方认证平台,24小时不间断提供最新高清电影、电视剧,无广告观看体验。
Copa del Rey livescore, Spanish cup competition with Real Madrid Barcelona action
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon on a daily basis.
It’s always exciting to read content from other writers and use
something from other sites.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.info/bn/register-person?ref=WTOZ531Y
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks! https://www.binance.com/es/register?ref=RQUR4BEO
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/bg/register-person?ref=V2H9AFPY
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
一帆平台AI深度学习内容匹配,专为海外华人设计,提供高清视频和直播服务。
愛海外版,專為華人打造的高清視頻平台運用AI智能推薦演算法,支持全球加速觀看。
官方授权的iyftv海外华人首选,第一时间提供最新华语剧集、美剧、日剧等高清在线观看。
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://accounts.binance.com/en-IN/register-person?ref=A80YTPZ1
真实的人类第三季高清完整版,海外华人可免费观看最新热播剧集。
愛壹帆海外版,專為華人打造的高清視頻官方認證平台,支持全球加速觀看。
艾一帆海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。
爱一帆会员多少钱海外版,专为华人打造的高清视频平台,支持全球加速观看。