Risk and Compliance Ultimate Guide: How to Manage Your Operations, Risks, and Compliance Obligations Effectively
Compliance is one of the most critical contributions to business success. Yet, many companies sideline this business function in favor of other important concerns, such as cashflow, profits and marketing. These companies often learn the hard way that compliance issues can create significant expenses in the form of fines. Violations can also have a long-lasting detrimental effect on a company’s reputation. Organizations that priorities compliance risks reap special benefits from understanding how to manage them.
What Is Risk Management?
The process of identifying, evaluating, and controlling risks to an organization’s strategic goals in the areas of finance, law, strategy, and security. The following is a list of possible sources of information for this article.
What Is Compliance Management?
Systems are continuously monitored and assessed by compliance management to ensure that they adhere to corporate and regulatory regulations and requirements, as well as industry and security standards.
Industry-Specific Compliance Risks
Many industries have laws and regulations specific to them, and each carries compliance burdens. For example:
- Banking. Banks must comply with regulations set by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corp. (FDIC), the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), and several other regulatory agencies. Financial firms also labor under laws such as the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), the Investment Companies Act, and the Dodd-Frank Act.
- Healthcare. Hospitals and other businesses that handle personal health information must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and reimbursement rules for government spending through Medicare and Medicaid.
- Pharmaceuticals. The pharmaceutical industry has extensive quality control obligations under the Food & Drug Act, Medicare & Medicaid rules, and HIPAA privacy rules.
- Consumer products. Manufacturers must comply with the Consumer Products Safety Act, plus various state consumer protection laws throughout the United States and overseas.
- Retailers. Retail operations that process credit card transactions must abide by the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) to keep credit card data secure or risk losing their ability to process such transactions.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Compliance Risk Management Program
When creating a risk management program, a thorough risk assessment is crucial. Any actions that might potentially result in hazards to regulations, reputation, and finances should be examined as part of this. Any systemic flaws that might result in non-compliance with the rules should also be found during the risk assessment.
Apply the following recommendations to guarantee an efficient assessment:
- Participate in the process with all necessary parties, including the legal and financial teams.
- Perform a careful examination of all operations that could be impacted by compliance rules.
- Determine areas that require improvement by analyzing internal strategies for potential hazards.
- Evaluate upcoming or recent changes to the law and regulations to see how they could affect your business.
- Analyze the organization’s capacity for prompt and efficient response to compliance-related concerns.
- Create a strategy for assessing the compliance management system’s performance and monitoring it.
Perform a risk analysis of the compliance management system to ensure that no new vulnerabilities are added to the final plan.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Effective Risk and Compliance Management is Critical for Your Business
Top issues for financial businesses in managing compliance and risk
According to the findings of a Wolters Kluwer study, significant regulatory compliance and risk problems continue to be significant for U.S. banks and credit unions in a number of important areas.
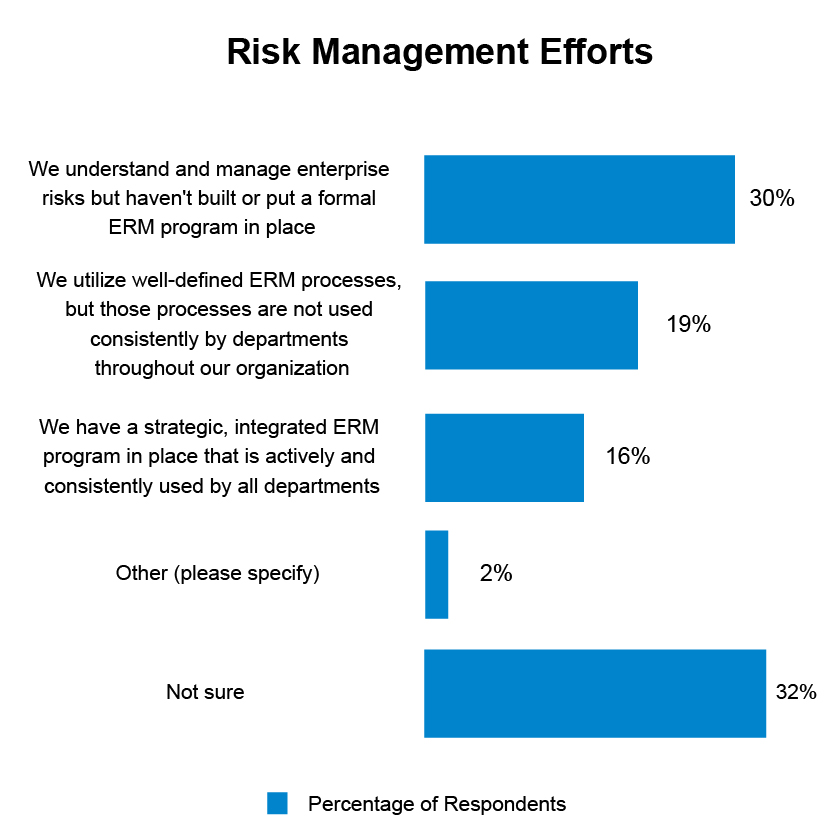
One of the many difficulties firms have with risk and compliance management is keeping up with constantly changing laws and regulations. Other difficulties include managing numerous compliance duties across several jurisdictions, making sure all workers are aware of and follow compliance obligations, and recognizing and minimizing possible risks before they become problems.
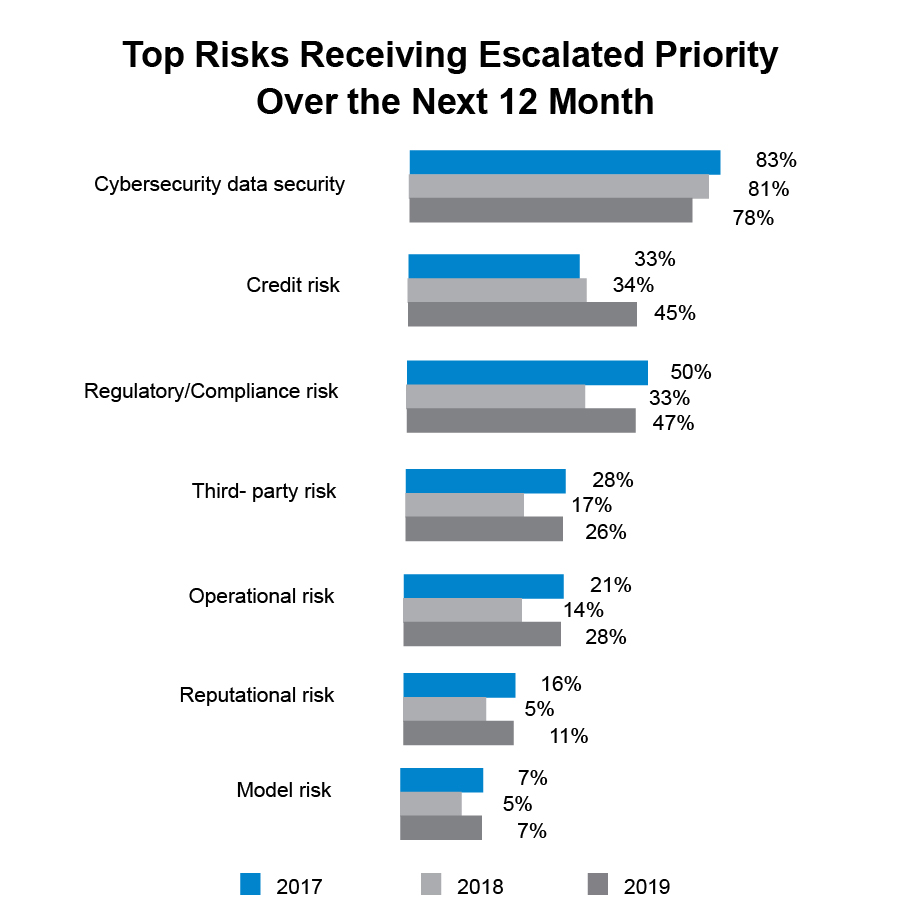
Moreover, compliance requirements might differ significantly by industry, firm size, and other considerations. It may be challenging for a small firm to remain on top of compliance duties, for instance, if it has the funds to engage a full-time compliance officer or set up a compliance management system.
5 Best Practices for Effective Risk and Compliance Management
Notwithstanding the difficulties, keeping the confidence of consumers and stakeholders depends on good risk and compliance management. The following are the recommended practices for a successful event.
- Regularly review and update policies and procedures to comply with changing regulations and laws
To guarantee compliance, it’s critical to continually evaluate and update policies and processes. Rules and legislation are always changing. This entails keeping abreast of modifications to the rules and legislation that apply to your company as well as periodically evaluating and revising your own policies and procedures.
2. Implement a compliance management system to centralize compliance obligations across jurisdictions
Businesses may more easily keep on top of regulatory and legal requirements by centralizing compliance duties across several countries with the use of a compliance management system. Moreover, real-time reporting and tracking capabilities offered by compliance management systems may assist organizations in spotting and resolving compliance concerns before they escalate into bigger difficulties.
- Conduct risk assessments and implement controls to mitigate potential risks
Businesses may identify possible risks and create measures to manage them with the use of risk assessments. This entails determining the areas with the biggest compliance risks and putting controls in place to lower those risks. Businesses may priorities compliance activities and spend resources more effectively by using risk assessments.
- Provide regular training and communication to employees to ensure they understand and adhere to compliance obligations
All staff members must be on board with the strategy and take part in managing risk and compliance effectively. All personnel should be able to comprehend and follow their compliance requirements with the support of regular training and communication. This entails educating staff members about compliance guidelines and practices and keeping them updated via regular communications.
- Conduct regular audits and assessments to ensure ongoing compliance and identify areas for improvement
Businesses may maintain continuing compliance and pinpoint opportunities for improvement by conducting regular audits and evaluations. This entails carrying out internal audits of compliance rules and practices in addition to external evaluations by outside auditors. Businesses may remain on top of compliance requirements and find opportunities for improvement with the aid of routine audits and assessments.
Case Studies: Examples of Businesses That Effectively Manage Their Operations, Risks, and Compliance Obligations
Enterprise Risk Management Example in Banking
A risk management framework and a risk appetite statement serve as the two pillars around which Toronto-based TD Bank structures its risk management. The enterprise risk framework outlines risk management procedures for identifying, evaluating, and controlling risk as well as defining the risks the bank must manage. The bank’s readiness to accept risk in order to accomplish its growth goals is described in the risk appetite statement. The risk committee of the company’s board of directors is in charge of both pillars.
The International Organization for Standardization’s (31000) standard, which has subsequently been modified, included risk management frameworks as a significant component. The standards offer general recommendations for risk management initiatives.
Also, the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission’s activities led to the creation of risk management frameworks (COSO). The organization was formed to combat corporate fraud, and one of its focuses was risk management.
TD moves on to the risk appetite statement after finishing the ERM framework.
The bank, which established a sizable foothold in the United States through significant acquisitions, decided that it will only take on risks that satisfy the following three requirements:
- The risk is appropriate for the company’s plan, and TD can recognize and control it.
- The risk does not expose the bank to a high danger of suffering a sizable loss.
- The danger does not put the business at risk of damage to its reputation and brand.
Strategic risk, credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, insurance risk, capital adequacy risk, regulator risk, and reputation risk are a few of the significant hazards the bank confronts. These categories are described by managers in a risk inventory.
Annual reviews are conducted of the risk framework and appetite statement, which are monitored on a dashboard against indicators including capital adequacy and credit risk.
To mitigate risk, TD employs a three lines of defense (3LOD) strategy, a technique that is well regarded among ERM professionals. These are the three lines:
- A business unit and corporate policies that implement controls, manage risk, and keep track of it.
- Rules and oversight that ensure risk monitoring, evaluation, and adherence to the risk appetite and framework.
- Internal reviews that independently confirm the effectiveness of risk-management practices.
Enterprise Risk Management Example in Retail
The largest retailer in the world is Walmart. Given the geographic dispersion of its activities, the quantity of stores it operates, the size of its supply chain, and its prominence as an employer and consumer of goods, the firm is aware that its risk profile is complicated.
The business desired a more straightforward approach to risk assessment in the 1990s, so it developed an enterprise risk management plan with five processes based on these four questions:
- What are the risks?
- What are we going to do about them?
- How will we know if we are raising or decreasing risk?
- How will we show shareholder value?
These five steps make up the procedure:
- Risk Identification: In seminars, senior Walmart officials identify hazards that are later depicted on a likelihood vs. effect graph. By doing this, the greatest risks may be given priority. Next, the executives examine seven internal and external risk categories: legal/regulatory, political, business environment, strategic, operational, financial, and integrity. Risk registers are often used by ERM experts to assess and rank hazards. You can get in touch with us, and we can help you with the “Free Risk Consultation Plan” by correlating risk likelihood and possible effect.
- Risk Mitigation: Teams with operational employees from the concerned region gather. To handle the hazards and evaluate the efficacy of the current inventory techniques, they employ them.
- Action Planning: Throughout the course of the ensuing months, a project team determines and puts into action the subsequent phases.
- Performance Metrics: To gauge the effects of the adjustments, the group creates metrics. They also observe patterns in actual performance over time in comparison to the objective.
- Return on Investment and Shareholder Value: To ascertain if the adjustments increased shareholder value and ROI, the team evaluates the impact of the changes on sales and costs in this stage.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I identify potential risks for my business?
- Conduct a risk assessment by analyzing internal and external factors that could impact your business.
What is compliance and why does my business need to comply with regulations?
- Compliance refers to a company’s adherence to laws, regulations, and industry standards. Non-compliance can result in financial and legal consequences.
What regulatory requirements do businesses need to comply with?
- Depending on the business’s location and sector, different regulations apply.
How can I effectively manage enterprise risks and ensure process controls?
- Establish a framework for risk management, evaluate risks often, and put controls in place to reduce recognized risks.
What are some common operational challenges faced by businesses?
- Common operational difficulties include quality control problems, security breaches, and interruptions in the supply chain.
How can I manage third-party relationships and mitigate associated risks?
- Establish explicit expectations and standards, perform due diligence on possible partners, and monitor the partnership for compliance and risk.
What are some best practices for strengthening IT processes to improve compliance and risk management?
- Establish tight access restrictions, monitor and test systems often, and educate staff about cybersecurity.
How can I prevent fraud and misconduct in my business?
- Create a code of conduct, put in place tight internal controls, and train staff members.
How can I align my cost base with falling revenues and manage financial risk?
- Develop a financial risk management strategy, diversify your sources of income, and put cost-cutting measures into action.
What are some strategies for managing manpower issues and challenges?
- Strategies for handling workforce concerns and challenges include staff retention initiatives, efficient recruitment techniques, and employee development and training.
What is business restructuring and how can it help manage risk and compliance?
- Making major adjustments to a business’s operations, structure, or finances is known as business restructuring. By increasing effectiveness and lowering costs, it may aid in risk and compliance management.
Why is developing a sustainability strategy important for my business?
- Creating a sustainability strategy may boost a company’s reputation, lower expenses, and lessen hazards to the environment and society.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with regulatory requirements?
- Non-compliance may have negative effects on a company’s reputation in addition to financial penalties and legal action.
How does technology play a role in risk management and compliance?
- Process automation, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance monitoring are all made possible by technology.
How we can help!
At JCSS in Indonesia, we help you rethink risk and compliances, develop strategies and enhance value, opening the doors to vast opportunities. JCSS has been rendering advice to over 450 clients spread across a broad spectrum of industries ranging from Infrastructure to Manufacturing, Construction to Information Technology. Our portfolio of clients ranges from starting companies in India, Indonesia, Japan & Singapore.

