Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
As we venture deeper into the digital age, the importance of cybersecurity has never been more apparent. With the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, it’s crucial to stay informed and motivated to protect your digital assets. In this article, we’ll explore the top cybersecurity risks of 2023, providing you with a comprehensive cybersecurity threat ranking and insights into emerging cybersecurity threats. By understanding the list of cybersecurity risks and staying up to date with cybersecurity predictions for 2023, you’ll be better equipped to safeguard your digital world.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks continue to be one of the most common cybersecurity attacks, with a significant increase in sophistication and frequency. Cybercriminals are now targeting larger organizations and critical infrastructure, causing widespread disruption and financial loss. Stay vigilant and invest in robust security measures to protect your data from these malicious attacks.
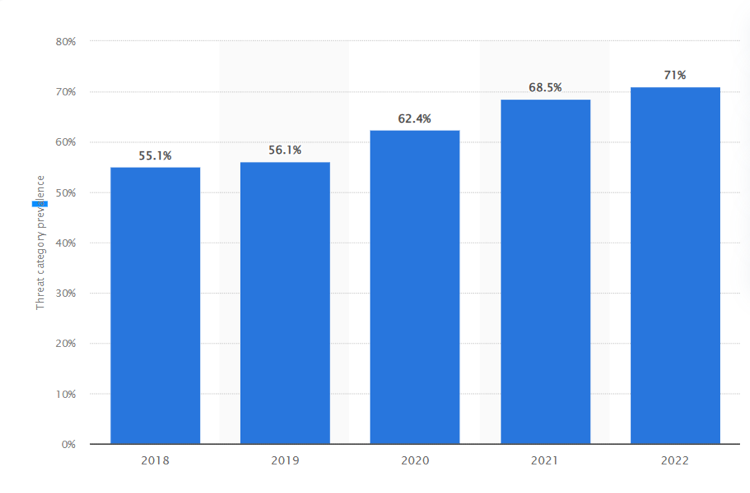
Image Source: Statista

Supply Chain Attacks
As seen in recent years, supply chain attacks have become a major cybersecurity vulnerability. Cybercriminals exploit weaknesses in third-party vendors and suppliers to gain access to their targets’ systems. Strengthen your supply chain security by conducting regular audits and ensuring your partners adhere to strict security standards.
AI-Powered Cyber Attacks
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has led to the emergence of AI-powered cyber-attacks. These attacks leverage machine learning algorithms to bypass traditional security measures and adapt to new defenses. Stay ahead of the curve by incorporating AI-driven security solutions into your cybersecurity strategy.
IoT Device Vulnerabilities

Insider Threats
Insider threats, whether intentional or accidental, pose a significant risk to organizations. Implement strict access controls, monitor user activity, and provide regular cybersecurity training to mitigate the risk of insider threats.
Read More: GRC Automation
Read More: Cyber Assurance & ISA
Cloud Security Breaches
As more businesses migrate to the cloud, cybersecurity vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure have become a growing concern. Ensure your cloud provider follows the best security practices and implement additional security measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Mobile Device Attacks
With the increasing reliance on mobile devices, cybercriminals are targeting smartphones and tablets to gain access to sensitive data. Protect your mobile devices by installing security apps, keeping software up-to-date, and avoiding public Wi-Fi networks.
Adware accounted for 25.28% of incidents, according to Kaspersky. This is backed up by the detection of 405,684 malicious installation packages. 75% of phishing sites are specifically designed for mobile devices, according to Zimperium. This is concerning given that 53% of mobile devices have access to more sensitive data.
Mobile app stores are taking measures to combat this, with Google and Apple blocking 1.2 million and 1.6 million suspicious applications, respectively, as reported by Checkpoint and ZDNet.
User behavior also plays a role in mobile security breaches, with 44% of companies that suffered a mobile security breach attributing it to user behavior, according to Verizon.
Interestingly, 18% of phishing email clicks come from a mobile device, underscoring the need for mobile security measures.
The global mobile security market is expected to reach $14.82 billion by 2028. Mobile users in Australia and Iran face significant threats, with encounter rates of 27% and 24% with mobile app threats, respectively.
Magazines’ mobile apps had the largest number of trackers, while YouTube and TikTok had the largest number of trackers among social media apps. It’s important to note that 41% of companies allow employees to use their own phones to access corporate systems and data, creating further challenges for mobile security.

Social Engineering Attacks

Deepfake Technology
Deepfake technology has advanced rapidly, allowing cybercriminals to create convincing fake videos and images for nefarious purposes. Stay informed about the latest deepfake detection techniques and invest in tools to identify and combat deepfake content.
Quantum Computing Threats
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize technology, but it also poses a significant risk to current encryption methods. Stay informed about quantum-resistant encryption algorithms and be prepared to adapt your security measures as quantum computing becomes more accessible.

Cybersecurity threats are becoming more sophisticated and complex as technology advances. It is crucial to stay informed about the latest threats and take proactive measures to protect your organization. In this article, we will discuss recent cybersecurity threats, solutions, unsolved threats, the use of AI in cybersecurity, the use of big data analytics, and how to prevent your organization from the ever-changing creative threats.
Recent Cybersecurity Threats and Solutions: The number of cyberattacks and data breaches has increased in recent years, targeting both public and private sectors. Some of the most common recent cybersecurity threats include ransomware attacks, phishing, and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
To mitigate these threats, organizations need to implement robust cybersecurity measures, including employee education and awareness, access controls, encryption, and intrusion detection and prevention systems.
Additionally, organizations should keep their systems and software up to date with the latest patches and updates to address vulnerabilities.
Unsolved Cybersecurity Threats : Some cybersecurity threats remain unsolved due to their complexity, stealthies, and unpredictability. These include zero-day exploits, which target unknown vulnerabilities in software and systems, and insider threats, where employees intentionally or unintentionally compromise security.
Another unsolved threat is the growing sophistication of AI-powered attacks, which can evade traditional security measures and learn to adapt to defensive measures.
Use of AI in Cybersecurity : AI has emerged as a powerful tool in the fight against cyberattacks, providing organizations with the ability to detect and respond to threats in real-time. AI-powered solutions can identify and classify threats, analyze data patterns and behaviors, and predict future attacks.
However, the use of AI also poses certain risks, including the potential for AI systems to be hacked, manipulated, or biased. Therefore, it is crucial to implement robust security measures to safeguard AI systems.
Use of Big Data Analytics : Big data analytics can provide valuable insights into potential threats and help organizations to identify patterns and trends that may indicate an attack. By analyzing large volumes of data, organizations can gain a better understanding of their network traffic, user behaviour, and system vulnerabilities. However, managing and analyzing big data requires sophisticated tools and techniques, including machine learning algorithms and data mining techniques.
Preventing Creative Threats : Preventing creative threats requires a multi-layered approach that includes people, processes, and technology. This includes regular employee training and education on cybersecurity best practices, such as strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and how to identify and report suspicious activity.
Additionally, organizations should implement access controls, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and encryption to protect their systems and data from cyberattacks. Finally, organizations should regularly conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and address potential weaknesses in their systems.
Conclusion
FAQS
How many cyber-attacks happen per year?
It is estimated that 2023 will face around 33 billion account breaches. Cyber-attacks 8,00,000 have been recorded in total, and on average, there is a hacker attack every 39 seconds.
Cyber-attacks on banks statistics?
20 million banking cyberattacks have been found and blocked according to Kaspersky. 79% of IT professionals believe the banking sector is a soft target for darknet operators.
How many cyber-attacks happen per day?
Around 2328 cybercrimes are thought to occur each day. Over the last 21 years from 2001 to 2021, cybercrime has claimed at least 6.5 million victims with an estimated loss of nearly $26 billion over the same period
Contact Us Now to schedule a free consultation and take the first step towards a more secure business.

